Contracting ITensors
Tensor contraction is often the most costly step of tensor algorithms. Code for contracting tensors can be fragile and error-prone when the tensor interface depends on the index ordering.
ITensor gets around these issues by using "intelligent" indices which recognize each other and automatically contract, regardless of the order they are in. ITensor works behind the scenes to make sure this is done as efficiently as possible.
To contract two ITensors, use
the * operator, which contracts all matching indices.
Some pairs of indices may match, yet you do not want them to be
contracted. To prevent this from happening, change the prime
level of such indices on one or both tensors as in the
second example below.
A Simple Example
Given three distinct Index objects i,j, and k, say we make the following ITensors:
auto A = ITensor(i,j);
auto B = ITensor(k,j);
Then the following code contracts over the index j
auto C = A * B;
In traditional notation this means performing the sum
If there had been other matching indices
between A and B other than j, the * operator would have contracted
them too. Indices i and k did not match (they could be copies of the
same Index but we are assuming this is not the case) so they remain
uncontracted and become the indices of C.
Interestingly, because of the way ITensor contraction is defined,
B*A gives the same result as A*B.
ITensor contraction is a commutative operation.
A More Complex Example
Of course, the real usefulness of a tensor library is handling cases where tensors have three or more indices.
Say we have an ITensor with indices i,s, and j
auto W = ITensor(i,s,j);
and want to contract W with itself, summing over indices i and j, but leaving s uncontracted.
In traditional tensor notation, we want to compute
But this notation can become cumbersome for more complicated contractions.
A nicer way to notate a tensor contraction is by using a diagram
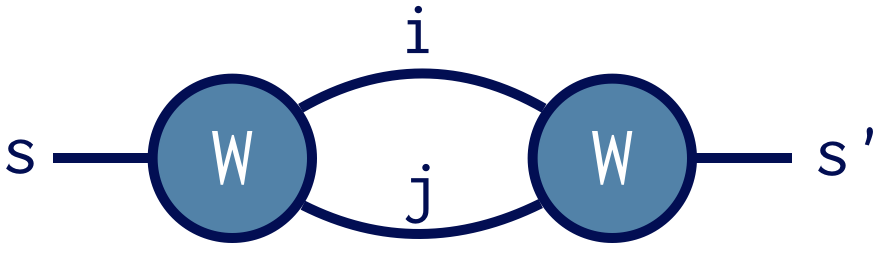
In diagram notation a tensor is a blob and each line denotes an index. Connecting two lines implies those indices are summed over. The remaining unpaired lines are the indices of the resulting tensor.
Both notations indicate our contraction strategy should be to
prime the Index s on one copy of W. Calling prime(W,s) returns
a copy of W with s replaced by s'. Then multiplying
auto D = W * prime(W,s);
automatically contracts i and j, but not s and s' since these no longer compare equal. Printing the result D confirms that it has only s and s' as indices.
 ITensor Basics
ITensor Basics
 Factorizing ITensors
Factorizing ITensors